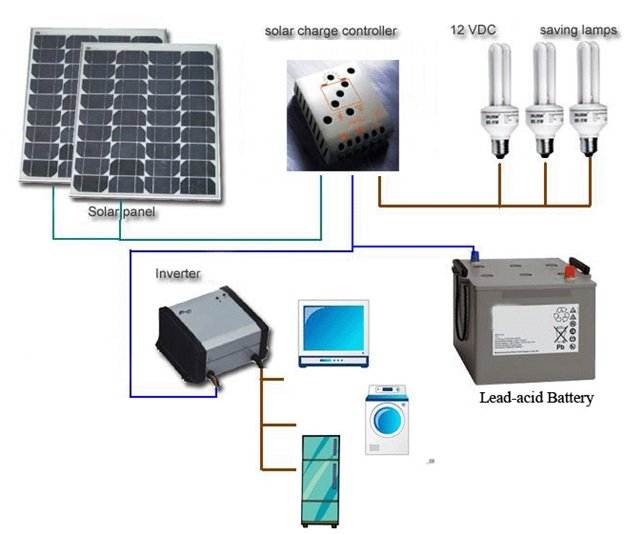
SOLAR INVERTOR
Abstract
Solar Photovoltaic is the technology by which solar energy is converted into electrical energy and its major applications in industrial and commercial sectors are; Solar Homes Systems upto 2000 W, Solar Lighting, Solar Power Plants from 10 KW to 20 MW, Solar Parks upto 20 MW, Solar UPS, Solar Roof Based On Grid Power Generation, Solar Traffic Signals Lights, Power for Remote Terminal Units, Power for Telecommunication Towers and BSC and MSC, Building Integrated Photovoltaic System, Military signaling applications, Solar water Pumping, Solar Lighting for Parking lots, Solar Lighting for Bus Stop Shelters etc.
It consists of a solar panel, which charges a battery and a inverter which can operate DC to AC and can operate up to four CFLs. SOLAR INVERTER An SOLAR INVERTER is an electrical device that converts solar radiation obtained from the sun directly into the direct current (DC) through the solar panel and then to alternating current (AC) by the use of inverter; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits. Solid-state solar inverters have no moving parts and are used in a wide range of applications, from small switching power supplies in computers, to large electric utility high-voltage direct current applications that transport bulk power. SOLAR inverters are commonly used to supply AC power from DC sources such as solar panels or batteries. A solar inverter or PV inverter is a critical component in a photovoltaic system. It converts the variable DC output of the solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current that can be fed into the commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network. An inverter allows use of ordinary mains-operated appliances on a direct current system. Solar inverters have special functions adapted for use with PV arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Stand-alone inverters, used in isolated systems where the inverter draws its DC energy from batteries charged by photovoltaic arrays. Many stand-alone inverters also incorporate integral battery chargers to replenish the battery from an AC source, when available. Normally these do not interface in any way with the utility grid, and as such, are not required to have anti-islanding protection. Grid tie inverters, which match phase with a utility-supplied sine wave. Grid-tie inverters are designed to shut down automatically upon loss of utility supply, for safety reasons. They do not provide backup power during utility outages. Battery backup inverters, are special inverters which are designed to draw energy from a battery, manage the battery charge via an onboard charger, and export excess energy to the utility grid. These inverters are capable of supplying AC energy to selected loads during a utility outage, and are required to have anti-islanding protection.